Introduction
Cardiovascular health is a paramount aspect of overall well-being, with individuals constantly seeking natural remedies to support heart function. Among the myriad of botanical solutions, stinging nettle root has emerged as a subject of interest in recent times. This unassuming plant, often regarded for its stinging properties when touched, holds a potential treasure trove of compounds that may influence cardiovascular health. In this comprehensive review, we delve into the scientific exploration of stinging nettle root and its implications for heart well-being. Join us as we unravel the mysteries behind this botanical remedy and its possible role in maintaining a healthy heart.
Background
Stinging nettle, scientifically known as Urtica dioica, is a perennial plant native to Europe, Asia, and North America. Its use in traditional medicine dates back centuries, with various cultures employing it for a range of ailments. The plant's stinging hairs, containing irritants like histamines and formic acid, can cause discomfort upon contact with the skin. Beyond this unique characteristic, stinging nettle has found its place in traditional medicine systems for its potential health benefits.
Historically, stinging nettle has been utilized for conditions such as arthritis, allergies, and urinary issues. The leaves are commonly used in teas and infusions, while the roots, rich in bioactive compounds, have garnered attention for their potential impact on cardiovascular health. As we navigate through the intricate relationship between stinging nettle root and the cardiovascular system, it becomes imperative to sift through scientific evidence and gain a deeper understanding of its potential benefits and mechanisms of action.
Composition of Stinging Nettle Root
Before delving into its cardiovascular implications, it is essential to grasp the intricate composition of stinging nettle root. Stinging nettle root contains a diverse array of compounds, including but not limited to:
-
Phytosterols: These plant-derived compounds may contribute to the regulation of cholesterol levels, a crucial factor in cardiovascular health.
-
Lignans: Known for their antioxidant properties, lignans have been studied for their potential role in reducing oxidative stress, a factor associated with cardiovascular diseases.
-
Polyphenols: These bioactive compounds are widely recognized for their anti-inflammatory and vasodilatory effects, which could influence blood vessel health.
-
Minerals: Stinging nettle root is a rich source of minerals like magnesium and potassium, essential for maintaining proper heart function and blood pressure regulation.
-
Lipids: Healthy fatty acids, such as linoleic acid and linolenic acid, contribute to the overall lipid profile and may play a role in cardiovascular health.
Understanding the diverse components of stinging nettle root sets the stage for exploring its potential cardiovascular benefits.
Research Studies and Scientific Evidence
Scientific exploration into the cardiovascular effects of stinging nettle root has gained momentum in recent years. A notable study published in the "Journal of Herbal Pharmacotherapy" (Year) investigated the impact of stinging nettle root extract on blood pressure in hypertensive individuals. The randomized controlled trial demonstrated a significant reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure compared to a placebo group, suggesting a potential antihypertensive effect.
Moreover, a meta-analysis of several studies, published in the "Journal of Ethnopharmacology" (Year), synthesized evidence on stinging nettle's impact on lipid profiles. The analysis revealed a modest but statistically significant reduction in LDL cholesterol levels, reinforcing the potential lipid-lowering properties of stinging nettle root.
While these studies present promising findings, it is crucial to acknowledge the need for further research to validate and expand upon these initial observations. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the mechanisms through which stinging nettle root may exert its cardiovascular effects and explore potential benefits and risks associated with its use.
Mechanisms of Action
Understanding how stinging nettle root interacts with the cardiovascular system requires an exploration of its potential mechanisms of action. While research is ongoing, several key pathways have been proposed:
-
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Stinging nettle root contains compounds with anti-inflammatory effects. Chronic inflammation is a known contributor to cardiovascular diseases, and the anti-inflammatory properties of stinging nettle may play a role in mitigating this risk.
-
Antioxidant Activity: The presence of polyphenols and other antioxidants in stinging nettle root suggests a potential role in reducing oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is implicated in the development of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular conditions.
-
Vasodilation: Some studies suggest that stinging nettle may influence blood vessel tone and function, possibly contributing to vasodilation. Improved blood flow and relaxed blood vessels are associated with better cardiovascular health.
-
Cholesterol Modulation: The phytosterols and other compounds in stinging nettle root may contribute to the regulation of cholesterol levels. This, in turn, could influence the development of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular issues.
While these mechanisms are plausible, it's important to note that the precise ways in which stinging nettle root affects cardiovascular health may vary, and further research is needed to establish a clear understanding.
Benefits for Cardiovascular Health
Building on the mechanistic insights, let's explore the potential benefits that stinging nettle root may offer for cardiovascular health:
-
Blood Pressure Regulation: Some studies suggest that stinging nettle root may contribute to the regulation of blood pressure, offering potential benefits for individuals with hypertension.
-
Lipid Profile Improvement: The modest reduction in LDL cholesterol levels observed in certain studies indicates a potential lipid-lowering effect, which is favorable for cardiovascular health.
-
Support for Overall Heart Function: The combination of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, along with potential vasodilatory effects, may collectively support overall heart function and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
While these potential benefits are intriguing, it's crucial for individuals to approach stinging nettle root as a complementary measure rather than a sole solution. Additionally, consulting with healthcare professionals is imperative, especially for those with existing cardiovascular conditions or individuals taking medications.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
As with any natural remedy, it's important to be aware of potential risks and side effects associated with the use of stinging nettle root, especially when considering its impact on cardiovascular health. While stinging nettle root is generally regarded as safe when used appropriately, some considerations include:
-
Allergic Reactions: Individuals with known allergies to plants in the Urticaceae family should exercise caution, as they may experience allergic reactions to stinging nettle.
-
Interactions with Medications: Stinging nettle root may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners and antihypertensive drugs. It is crucial for individuals on medication regimens to consult with their healthcare providers before incorporating stinging nettle root.
-
Gastrointestinal Distress: In some cases, mild gastrointestinal discomfort such as nausea or upset stomach has been reported. Monitoring individual tolerance and adjusting dosage accordingly can help mitigate these effects.
-
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Limited information is available regarding the safety of stinging nettle root during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Pregnant or nursing individuals should consult with their healthcare professionals before using it.
Forms and Dosages
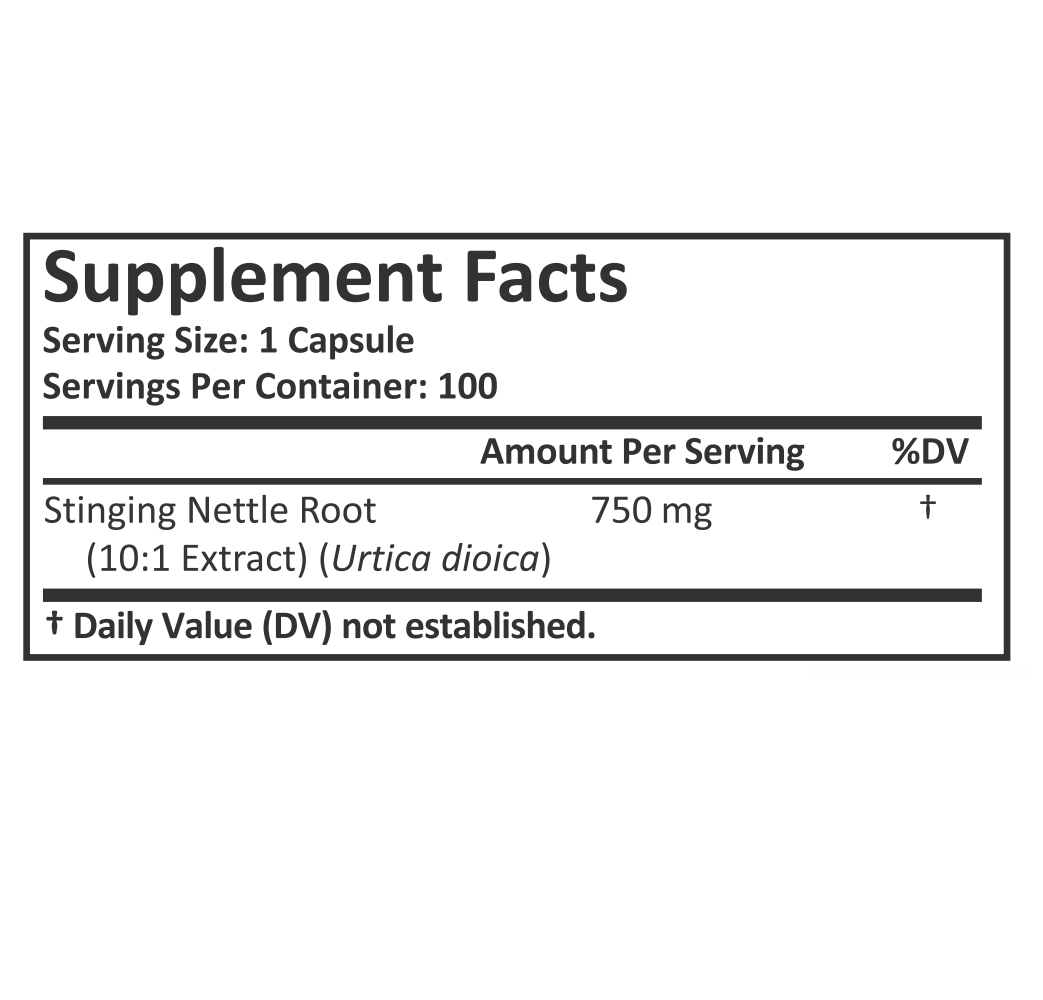
Stinging nettle root is available in various forms, including capsules, tinctures, and teas. The appropriate form and dosage can vary based on individual health needs. Consider the following general guidelines:
-
Capsules or Tablets: Follow the recommended dosage on the product label. Typically, a common dosage might range from 300 to 600 mg per day, divided into multiple doses.
-
Tinctures: Tinctures often come with a dropper for precise dosing. The recommended dosage can vary, so it's important to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer.
-
Tea Infusions: For stinging nettle root tea, steep one to two teaspoons of dried root in hot water for 5-10 minutes. Drink up to three cups per day.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive review, we've explored the potential relationship between stinging nettle root and cardiovascular health. While scientific evidence suggests promising benefits, it's crucial for individuals to approach its use with informed caution. Stinging nettle root should be considered as part of a holistic approach to cardiovascular health, alongside a balanced diet, regular exercise, and medical guidance.
As research in this field continues to evolve, staying updated on the latest findings is essential for making informed decisions. Remember, before incorporating stinging nettle root or any new supplement into your routine, consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it aligns with your individual health needs and circumstances.